Table of Contents
show
Loop Control statements change execution from its normal sequence. When execution leaves a scope, all automatic objects that were created in the scope are destroyed
Python supports the following loop control statements:
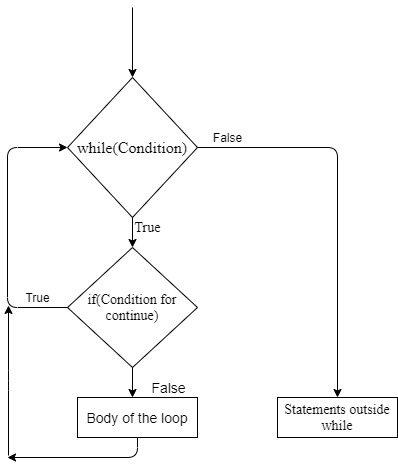
continue
It returns the control to the beginning of the loop,
Syntax,
while(test conition):
if(condition for continue):
continueFlowchart
Example
for i in "Learn Python":
if(i == "n"):
continue
print("current letter",i)Output,
current letter L
current letter e
current letter a
current letter r
current letter
current letter P
current letter y
current letter t
current letter h
current letter o
break
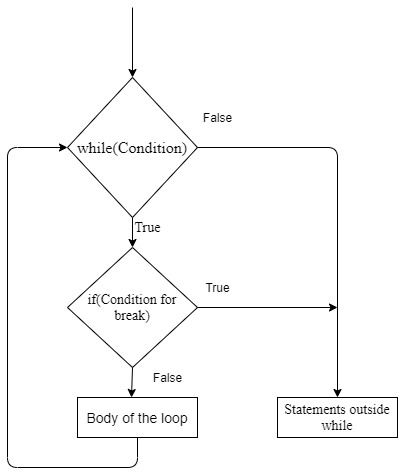
It brings control out of the loopIt terminates the current loop and executes the remaining statement outside the loopIf the loop has else statement, that will also gets terminated and come out of the loop completely
Syntax,
while(test conition):
if(condition for break):
breakFlowchart
Example
for i in "Learn Python":
if(i == "n"):
break
print("current letter",i)Output,
current letter L
current letter e
current letter a
current letter r
pass
pass statement is used to write empty loopsIt is used when a statement is required syntactically but you don’t want any code to executeIt is a null statement, nothing happens when it is executed
Syntax
passExample,
for i in "Learn Python":
pass
print("current letter",i)Output
current letter nDifference between break and continue
![]()
Views: 5