- Aliasing happens whenever one list’s value is assigned to another list
- An Alias is a second name for the list
- Since the list is mutable, aliasing can result in hard to find bugs
Example
Original_List = [1,5,2]
New_List = Original_List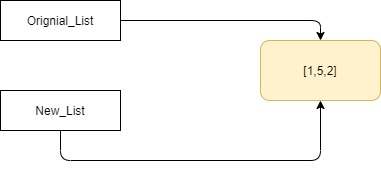
>>> first_list = [1,4.2,0,39,"Python"]
>>> second_list = first_list
>>> first_list
[1, 4.2, 0, 39, 'Python']
>>> second_list
[1, 4.2, 0, 39, 'Python']
>>> first_list[2] = 200
>>> first_list
[1, 4.2, 200, 39, 'Python']
>>> second_list
[1, 4.2, 200, 39, 'Python']second_list is the alias name of the first_list i.e. both the lists are pointing to the same object. Therefore, the changes made in first_list is reflected in second_list
![]()
Views: 1