Table of Contents
show
Arguments
The arguments that are given after the name of the program in the command line shell of the operating system are known as command line arguments
Various ways of using command line arguments are
- Using sys.argv
- Using getopt module
- Using argparse module
Using sys.argv
The sys module provides functions and variables used to manipulate different parts of the python runtime environment.
This module provides access to some variables used or maintained by the interpreter and to functions that interact strongly with the interpreter
Syntax
sys.argvIt is a simplest list structure. It’s main purposes are:
- It is a list of command line arguments
- len(sys.argv) provides number of command line arguments
- sys.argv[0] is the name of the current python script
Example
To add numbers passed in command line arguments
import sys
# total arguments
n = len(sys.argv)
print("Total arguments passed:", n)
# Arguments passed
print("\nName of Python script:", sys.argv[0])
print("\nArguments passed:", end = " ")
for i in range(1, n):
print(sys.argv[i], end = " ")
# Addition of numbers
Sum = 0
# Using argparse module
for i in range(1, n):
Sum += int(sys.argv[i])
print("\n\nResult:", Sum)Output
o sys.argv[0] – file name
o sys.argv[1] contains 20
o sys.argv[2] contains 30
o sys.argv[3] contains 40
o sys.argv[4] contains 50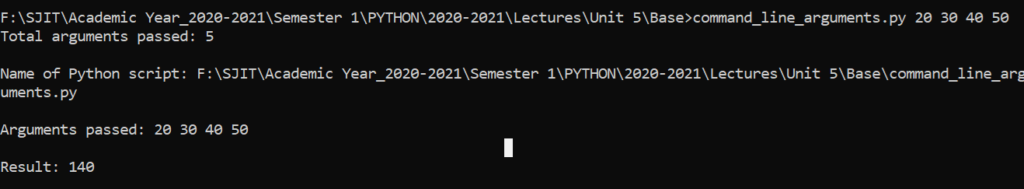
Views: 1