Table of Contents
show
Write a python script to display current date and time
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now()
print ("Current date and time : ")
print (now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"))Output
Current date and time :
2021-02-22 20:01:01Description
The datetime module supplies classes for manipulating dates and times in both simple and complex ways. datetime.now(tz=None) returns the current local date and time. If optional argument tz is None or not specified, this is like today(). date.strftime(format) returns a string representing the date, controlled by an explicit format string. Format codes referring to hours, minutes or seconds will see 0 values.
Design a python code to count number of words in a python file
file = open("myfile1.txt", "r")
data = file.read()
words = data.split()
print('Number of words in text file :', len(words))Input file: myfile1.txt
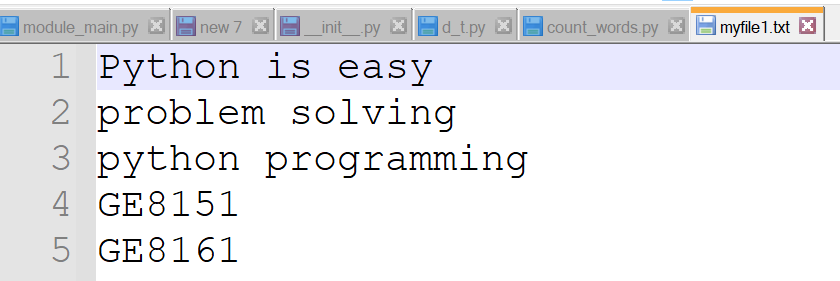
Output
Number of words in text file : 9Write a python user defined function to find whether the given number is perfect number of not and return the result alone to a file (with and without command line arguments)
With command line arguments
def perfect():
n = int(input("Enter any number: "))
sum1 = 0
for i in range(1, n):
if(n % i == 0):
sum1 = sum1 + i
fp = open("sum1.txt","w")
if (sum1 == n):
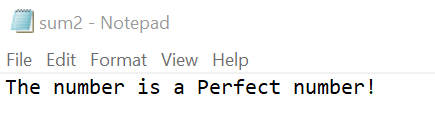
fp.write("The number is a Perfect number!")
else:
fp.write("The number is not a Perfect number!")
print("Result written successfully sum1.txt")
fp.close()
perfect()Output
Result written successfully sum1.txt

Without command line arguments
import sys
def perfect():
n = int(sys.argv[1])
sum1 = 0
for i in range(1, n):
if(n % i == 0):
sum1 = sum1 + i
fp = open(sys.argv[2],"w")
if (sum1 == n):
fp.write("The number is a Perfect number!")
else:
fp.write("The number is not a Perfect number!")
print("Result written successfully")
fp.close()
perfect()Output

Write a function that copies a file reading and writing up to 50 characters at a time
def read_write_50():
with open('myfile1.txt') as f:
f1=open("write50.txt","w")
while True:
# Read from file
c = f.read(50)
f1.write(c)
if not c:
break
# print the character
print(c)
read_write_50()Output
Python is easy
problem solving
python programmin
g
GE8151
GE8161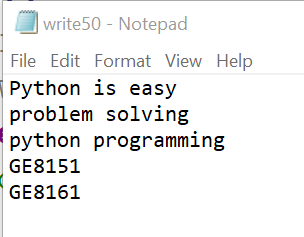
How to merge multiple files to a new file using python?
filenames = ['file1.txt', 'file2.txt', 'file3.txt']
with open('output_file', 'w') as outfile:
for fname in filenames:
with open(fname) as infile:
outfile.write(infile.read())
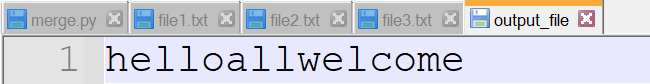
print("data written successfully")Input files
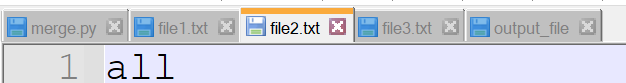
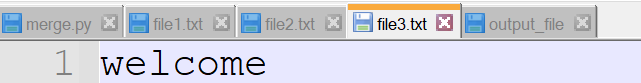
Output
data written successfully
Write a python program to copy the contents of text file to another text file using command line arguments
import sys
with open(sys.argv[1]) as f:
with open(sys.argv[2], "w") as f1:
for line in f:
f1.write(line)
print("Data written successfully")Input Files

Output

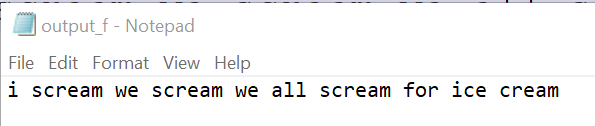
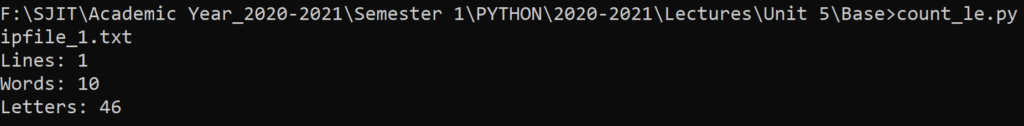
Write a python program to count number of lines, words and characters in a text file using command line arguments
import sys
fname = sys.argv[1]
lines = 0
words = 0
letters = 0
for line in open(fname):
lines += 1
letters += len(line)
pos = 'out'
for letter in line:
if letter != ' ' and pos == 'out':
words += 1
pos = 'in'
elif letter == ' ':
pos = 'out'
print("Lines:", lines)
print("Words:", words)
print("Letters:", letters)Input Files

Output
Write a sample snippet to write hello world to end of existing file
f1 = open("ipfile_1.txt","a")
f1.write("Hello World")
print("data appended")
f1.close()Output
data appended

Views: 1