Template matching is used to locate the occurrence of a smaller image (called a template) within a larger image
Finding a part of an image that matches the given template
result = cv2.matchTemplate(image, templ, method)- image: The source image (input image) where you want to search for the template. It can be a single-channel (grayscale) or multi-channel (color) image.
- templ:The template image that you want to match against the source image.
- It must be of the same type as the source image and smaller in size.
- method:
- The method used for matching, which can be one of the following constants:
- cv2.TM_CCOEFF
- cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED
- cv2.TM_CCORR
- cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED
- cv2.TM_SQDIFF
- cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED
The result matrix will be of dimension:
- Width:
- result_width=image_width−template_width+1
- Height:
- result_height=image_height−template_height+1
For a template of size (template_width, template_height):
- The maximum x-coordinate for the top-left corner of the template is image_width – template_width.
- The maximum y-coordinate is image_height – template_height.
Original Image: Width = 1025, Height = 1367
Template: Width = 486, Height = 375
The valid top-left corner positions for the template would range:
- X-coordinates: 0 to 1025 – 486 = 539
- Y-coordinates: 0 to 1367 – 375 = 992
This means:
- The template can be placed starting from (0, 0) up to (539, 992) in the original image without any part of it exceeding the original image boundaries.
cv2.TM_SQDIFF
SQDIFF stands for Squared Differences, and it’s a method used in template matching in OpenCV (cv2.TM_SQDIFF)
- Lower values are better: The best match occurs where the squared differences are the smallest, meaning the template and the image region are most similar.
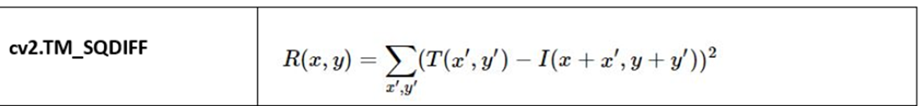
cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED
Normalized Squared Difference
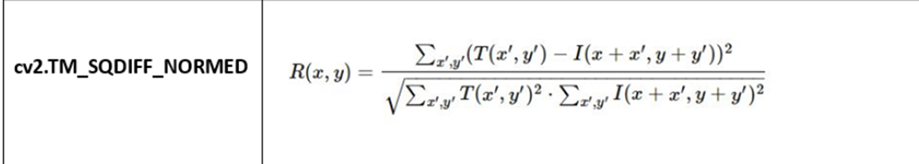
Lower values are better: The best match occurs are the smallest, meaning the template and the image region are most similar.
cv2.TM_CCORR
Cross Correlation – relies on similarity
Higher values are better: A higher score indicates a better match, meaning that the template and the image region are more similar.
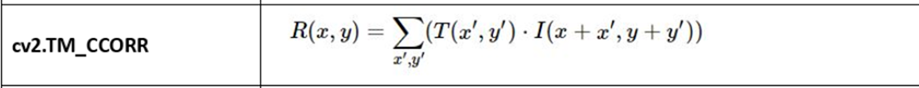
cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED
Normalized Cross Correlation
Higher values are better: A higher score indicates a better match, meaning that the template and the image region are more similar.
Higher values (closer to 1) indicate a better match.
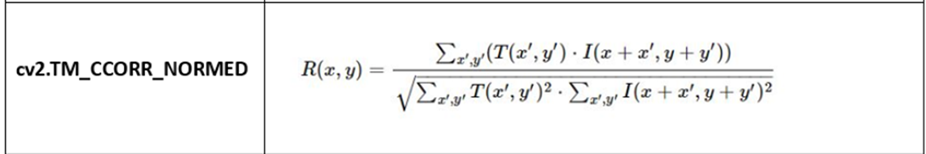
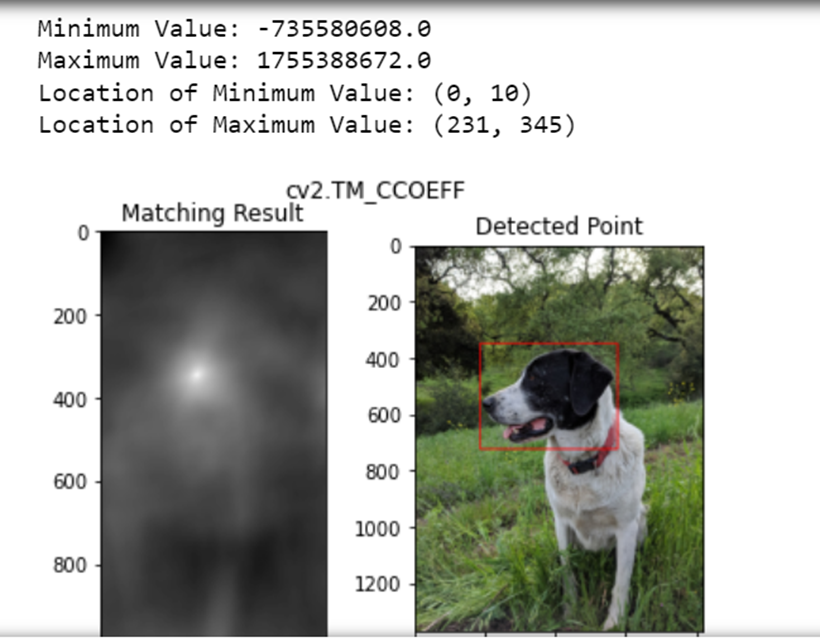
cv2.TM_CCOEFF
Cross Coefficient
- Higher values indicate a better match:
- Positive values represent good matches, and
- negative values represent poor matches.
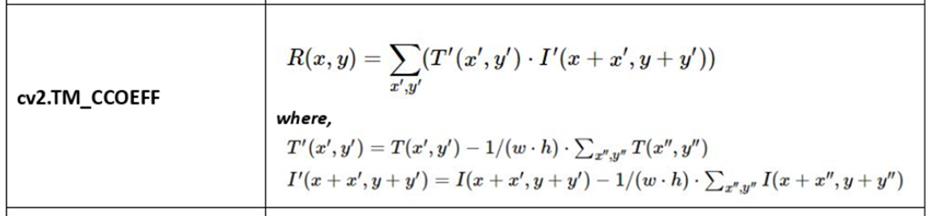
cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED
Normalized Cross Coefficient
- If the normalized score is close to 1, the image region closely matches the template.
- If the score is close to -1, the template is almost a negative (inverted) of the image region.
- A score of 0 means there is no correlation between the template and the image region.

Output returned by minMaxLoc( )
![]()
Views: 1