Table of Contents
show
- File is a named location on the system storage which records data for later access
- It is stored in a non-volatile memory
- A unique path name of the file must be given to access the file for reading and modification purpose
- C view’s each file as a sequential stream of bytes
- Each file ends with either an end – of file marker
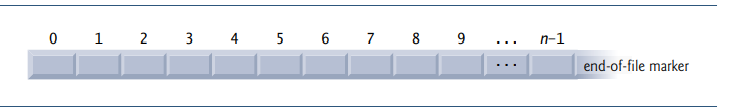
When a file is opened, a stream is associated with it.
Three streams are automatically opened when program execution begins:
- the standard input (which receives input from the keyboard),
- the standard output (which displays output on the screen) and
- the standard error (which displays error messages on the screen)
Communication Channels
Streams provide communication channels between files and programs.
For example, the standard input stream enables a program to read data from the keyboard, and the standard output stream enables a program to print data on the screen.
Files are classified into text file and binary file,
Text file:
- Text files are structured as a sequence of lines, where each line includes a sequence of characters.
- Each line is terminated with a special character, called the EOL or End of line character
- They are identified with .txt file
Binary File:
- Binary file is a file stored in binary format
- A binary file is machine – readable but not computer readable
- All executable programs are stored in binary files
- They are identified as .bin, .dat
File structure
- Opening a file returns a pointer to a FILE structure (defined in) that contains information used to process the file.
- In some operating systems, this structure includes a file descriptor, i.e., an integer index into an operating-system array called the open file table.
- Each array element contains a file control block (FCB)—information that the op[1]erating system uses to administer a particular file.
- The standard input, standard output and standard error are manipulated using stdin, stdout and stderr.
Views: 0